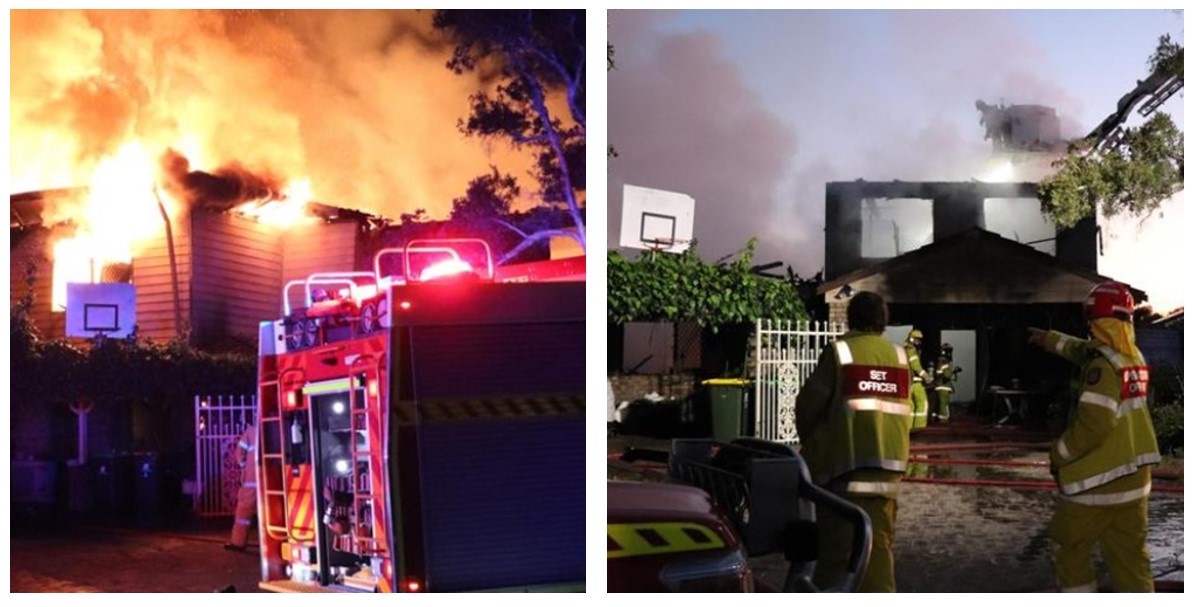
Properly working smoke alarms in Queensland could have saved lives in the recent tragedy on Russell Island, where a house fire claimed the lives of five young brothers and their father. Emergency services responded to the blaze on Todman Street, Brisbane’s Redland Bay, just after 6am on Sunday, 8th August, finding the two-storey home fully engulfed in flames, with two nearby properties also alight. A 21-year-old woman, believed to have been inside, managed to escape with injuries. This devastating incident highlights the importance of having working smoke alarms in Queensland homes to prevent such tragedies.
The Queensland Fire and Emergency Services Assistant Commissioner, John Cawcutt, said the blaze was “one of the worst fires we’ve had for a long time”. Fire and Emergency Services Minister Mark Ryan also said the fire was a great tragedy. “Of course a very sad day for Queenslanders,” he said. “Our hearts break for those involved in the tragedy. It seems a tragic loss of life”. A forensic investigation is currently underway to determine how the fire started, and why the smoke alarms did not activate.
A close family friend issued a harrowing plea to all Australians on the behalf of the Children’s surviving mother, stating that she ‘just wants the world to know – check your smoke alarms and hold your babies’.
In terms of sheer loss of life from a single domestic house fire, the Russell Island fire tragedy is second only to the August 2011 Logan house fire, which was Australia’s deadliest house fire, causing the death of 11 family members. A coronial inquest could not establish the exact cause of that blaze but a coroner found there was a ‘reasonable prospect’ that all or some of the victims could have escaped if smoke alarms had been working. That tragedy led to the introduction of new QLD laws for photoelectric interconnected smoke alarms inside every bedroom, hallways outside the bedrooms, and on every level of Queensland homes.
Why Didn’t The Smoke Alarms in Queensland’s
Russell Island House Fire Activate?
The rented two storey Queenslander home allegedly had smoke alarms installed, however the female survivor of the blaze said she didn’t hear any smoke alarms activate, adding that concerns had previously been expressed about them. Immediately after the fire it remained unclear why the fire alarms didn’t activate and whether they were in working order. ‘With a fire of that intensity it will be difficult to know whether there were smoke alarms present or not but that will be part of the investigation,’ Queensland Fire Department Deputy Commissioner Joanne Greenfield said.
It is understood the home was transported to the site around 2017. ‘So thinking about the legislation that was in place at that time it would have required one hardwired smoke alarm, that’s if it was following the legislation,’ QLD Fire Department Commissioner Leach said.
Development in the Russell Island house fire – why didn’t the smoke alarms activate?
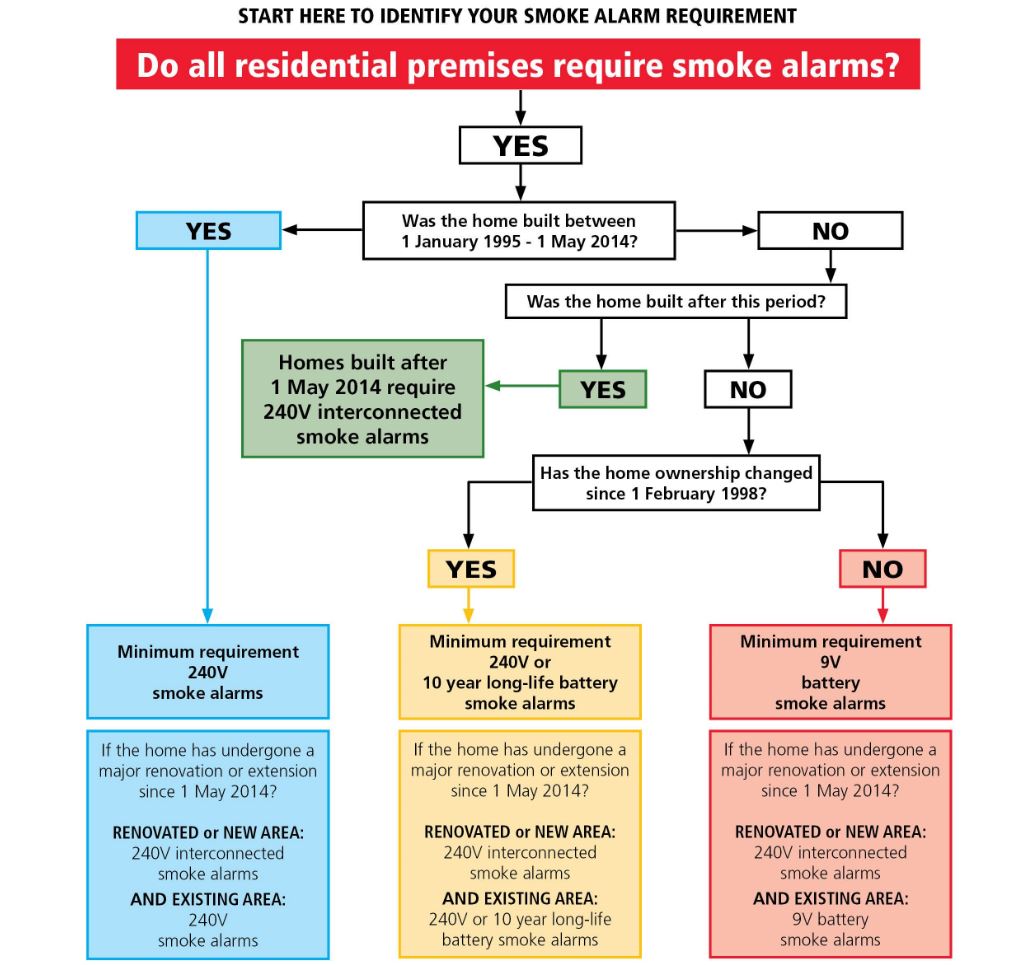
New Laws For Smoke Alarms in Queensland
From 1st January 2022, all properties being sold or leased for rent in Queensland were required by QLD law to have interconnected smoke alarms installed as per below (on 1st January 2027 the law is being extended to cover all QLD homeowners and occupiers, irrespective of whether the property is being sold or rented out).
Legal Requirements For Smoke Alarms in Queensland
Smoke alarms in Queensland must:
- be photoelectric (AS 3786-2014); and
- not also contain an ionisation sensor
- be less than 10 years old from manufacture date
- operate correctly when tested
- be interconnected with every other smoke alarm in the dwelling so all activate together
- be either hardwired or powered by a non-removeable 10-year battery
Where Must Smoke Alarms in Queensland Be Installed?
Smoke alarms in Queensland must be installed on each storey:
- inside every bedroom
- in hallways which connect the bedrooms and the rest of the dwelling
- if there is no bedroom on a storey, then at least one interconnected smoke alarm must be installed in the most likely travel path to exit the dwelling.
Rental Property Law For Smoke Alarms in Queensland
In addition to the above, rental property managers and landlords are required by QLD law (QLD Fire and Emergency Services Act 1990) to test and clean interconnected smoke alarms and replace any flat or nearly flat batteries within 30 days before the start of a tenancy. This also includes a renewal tenancy. The tenant must also test and clean smoke alarms in Queensland rental dwellings at least once every 12 months.
If the tenant is aware a smoke alarm in the dwelling has failed, the tenant must advise the lessor as soon as possible. It’s important for both parties to ensure that smoke alarms are maintained in optimal working condition to prevent potential fire hazards and ensure compliance with fire safety regulations. Failure to do so could result in penalties or compromise the safety of the property and its residents.

Smoke alarms in Queensland and rental property smoke alarm law
Postscript Update – April 2024
The landlord was charged and fined under the QLD Fire and Emergency Services Act 1990 after she admitted failing to install compliant photoelectric interconnected smoke alarms in the rental property.
The interstate landlord claimed to be unaware of the changes to QLD’s smoke alarm legislation.
“It’s absolutely no excuse that she failed to keep abreast of the laws required of an investment property owner in having the premises legally wired with smoke detectors after January 2022,” Magistrate Deborah Vasta said. Ms Vasta told the court that the landlord had failed to comply with safety legislation and a coronial inquest into the six deaths was still yet to occur.
“There’s no evidence about whether two smoke alarms that were there were working or not,” she said.
Detectives are continuing their investigation following the fire and a final report will be given to the coroner in the near future.

Want to know more? Watch our ZEN Smoke Alarm YouTube channel or call us on 0478 596 402 today
We love talking smoke alarms!
ZEN Interconnected Smoke Alarms
New Farm, QLD, 4005