Interconnected Smoke Alarms
And Australian Standard 3786:2014
Before buying an interconnected smoke alarm you should do your due diligence to ensure it is compliant to Australian Standard 3786:2014. The full name of the standard which encompasses smoke alarms in Australia is ‘Australian Standard 3786:2014 Smoke alarms using scattered light, transmitted light or ionization’ (incorporating amendment 1 and 2). This article will review Australian Standard 3786:2014 to assist your purchasing decision.
Standards are documents that set out specifications, procedures and guidelines to ensure products are safe, consistent, and reliable. Australian Standard 3786:2014 is referenced by QLD’s Building Fire Safety Regulations 2008 – when a standard is referenced by state or national legislation, compliance with it becomes mandatory. It is interesting to note that although there is a newer Australian Standard 3786:2023 – it is not yet referenced by legislation – therefore Australian Standard 3786:2014 must still be complied with in the eyes of the law.

Australian Standard 3786:2014 is divided into several key components – the area of interest that will be reviewed today is section 4.17 – ‘general requirements’.
Section 4.17 of the Australian Standard states that; ‘The smoke alarm shall be so designed that a sphere of diameter larger than 1.3 ±0.05 mm cannot pass into the sensor chamber(s)’. This requirement is intended to restrict the access of foreign bodies such as insects into the sensitive parts of the smoke alarm (to prevent nuisance alarms). It is known that this requirement is not sufficient to prevent the access of all insects; however, it is considered that extreme restrictions on the size of the access holes may introduce the danger of clogging by dust, etc.
Interconnected Smoke Alarms – Mesh Screen
How does this requirement translate into the design and manufacture of your photoelectric interconnected smoke alarm? The image below shows the compliant internal component from our ZEN wireless interconnected smoke alarm. The polymer mesh surrounding the sensitive photoelectric chamber within the alarm contains thousands of tiny holes, each perfectly engineered, no larger than 1.3mm in diameter. The tiny holes prevent insects from accessing the internal chamber whilst still allowing air (and smoke) to pass through.
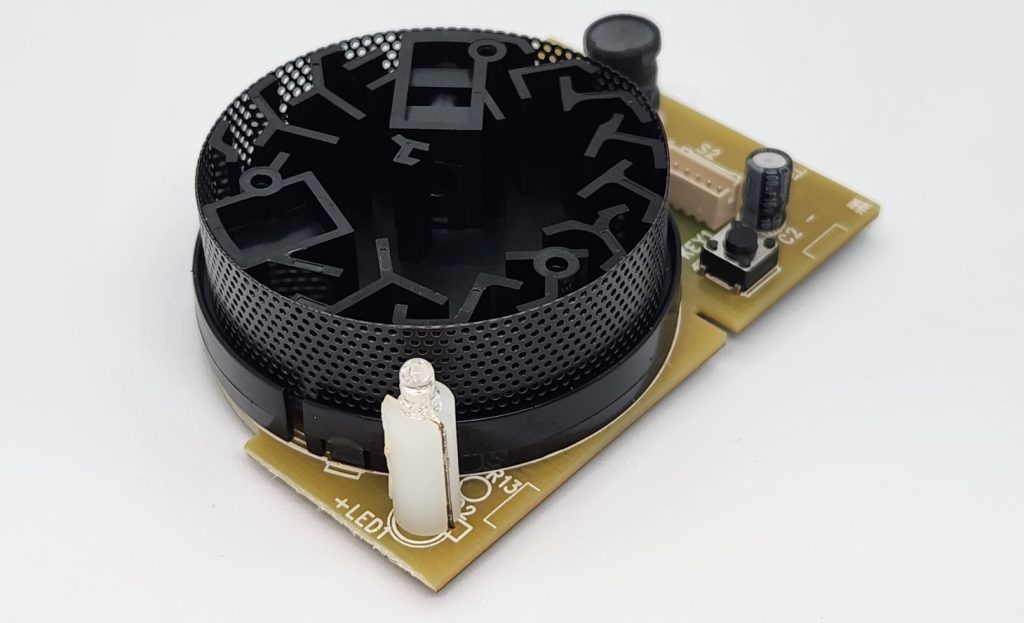

Mesh screen surrounding the photoelectric smoke alarm internal sensor chamber
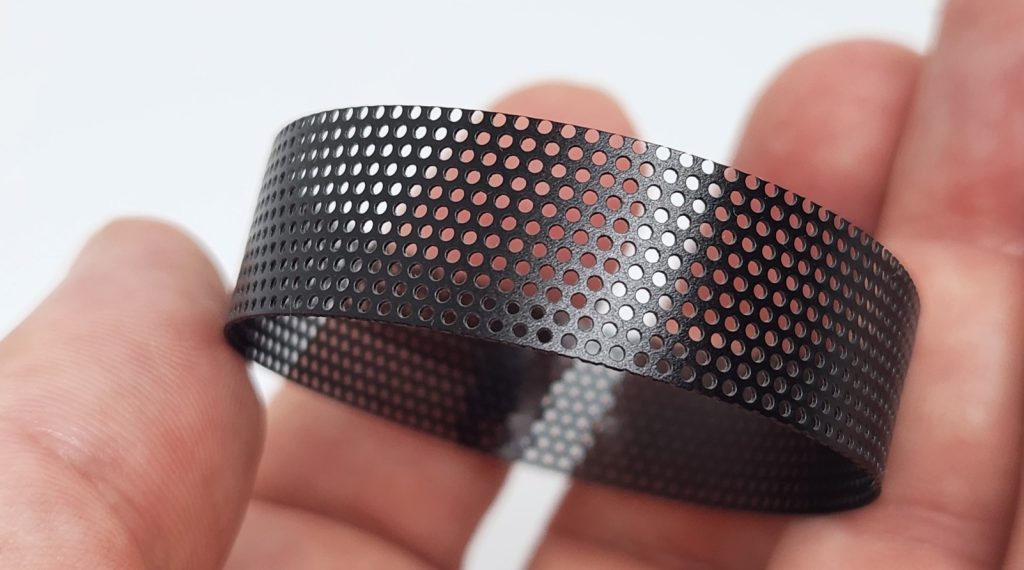
As per Australian Standard 3786:2014 – holes are no larger than 1.3mm diameter
In addition to this internal mesh screen around the perimeter of the photoelectric chamber, ZEN wireless photoelectric interconnected smoke alarms also have an external housing which forms part of the of the smoke alarm itself. The external housing prevents larger foreign bodies from entering the alarm itself. Foreign bodies (i.e., insects, small house geckos) are a common cause of false / nuisance alarms because they can enter the sensitive internal components and disrupt the photoelectric light beam.
We hope you have enjoyed this review of section 4.17 of Australian Standard 3786:2014, and how it translates to the design of your interconnected smoke alarm. Whilst many smoke alarm retailers might profess to be aware of the standard, very few can claim to have read it from cover to cover or have a genuine understanding of what it means.


Want to know more? Watch our ZEN quick-start video or call us on 0478 596 402
We love talking smoke alarms!

